35 W 36 Street, Suite 7 E New York, NY 10018
35 W 36 Street, Suite 7 E New York, NY 10018
This section will describe what you may feel (symptoms) or see (signs) if you’ve contracted syphilis.
Symptoms (what you feel)
As with any infectious disease, symptoms usually precede signs by a little. Symptoms are the sensations that you feel because of the disease process.
Signs (what you see)
Signs are things you and your healthcare provider can see that are caused by the disease process. Signs usually follow symptoms or come at the same time. Signs, unlike symptoms, are objective and therefore more trusted by doctors.
Knowing what the symptoms and signs of syphilis are might be helpful in reaching an early diagnosis and starting treatment.
Chancre is the localized skin symptoms of early syphilis. This stage lasts for one to two months. An initial local infection spreads quickly all over the body.
Incubation period
The incubation period for the chancre is 3 to 90 days (21 days on average).
From bump to ulcer to healing
Most common areas
The following chart shows where a syphilis chancre most commonly appears in in homosexual males.
22% of homosexual males get chancres in their rectum.

Other associated symptoms
Syphilis bump
This is a photo of a syphilis bump that will eventually (in seven days) ulcerate, forming the chancre (sore).
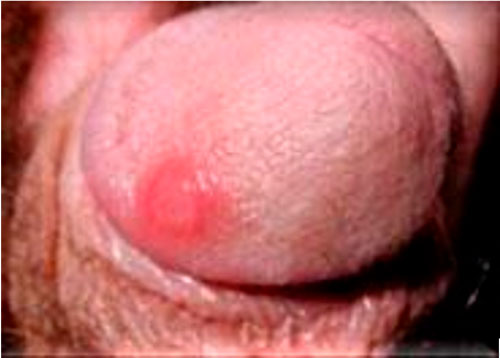
Image source: Ayurveda Treatment Venereal Diseases - KHOKAR. https://www.khokardispensary.com/ayurveda-treatment-venereal-diseases/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
Penile syphilis chancre
This photo is of a syphilis sore on the penile shaft. Note the raised, hard, well-defined borders and the clean base.
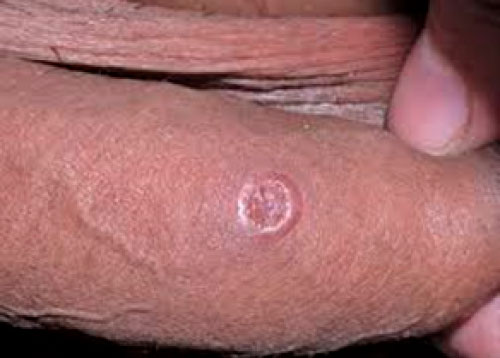
Image source: New York City Department of Health T, Hygiene Bureau of Sexually Transmitted Infections M. The Diagnosis, Management and Prevention of Syphilis An Update and Review STD HIV PREVENTION TRAINING CENTER.; 2019. https://www.cdc.gov/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
This image shows two syphilis sores with well-defined borders.
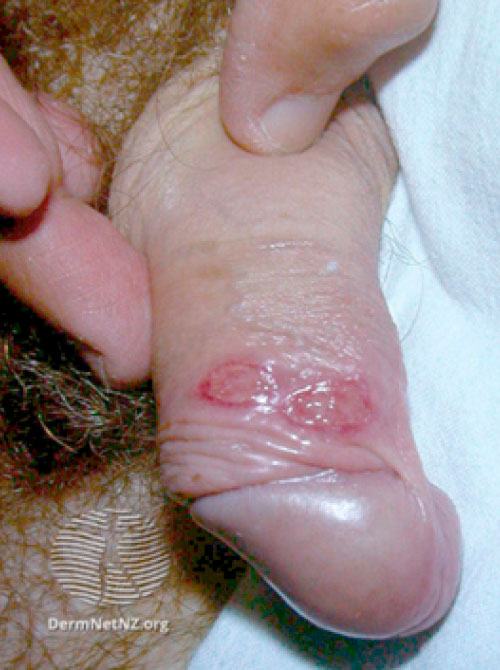
Image source: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer, 2003. Syphilis | DermNet NZ. Retrieved from https://dermnetnz.org/topics/syphilis/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
Vaginal chancre
Here is a photo of a syphilis sore on the vagina wall.
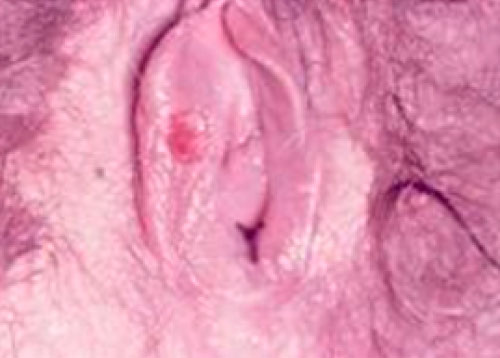
Image source: Ayurveda Treatment Venereal Diseases - KHOKAR. https://www.khokardispensary.com/ayurveda-treatment-venereal-diseases/. Accessed January 22, 2021.
Anal chancre
This image is of two syphilis sores near the anus. Note the hard, raised borders.
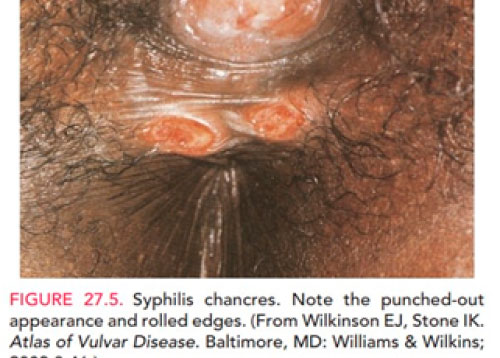
Syphilis sore on the lip
This photo shows a well-defined sore on the patient’s lip with raised, hard borders. “Well-defined” means there is a clear separation from the rest of the lip.
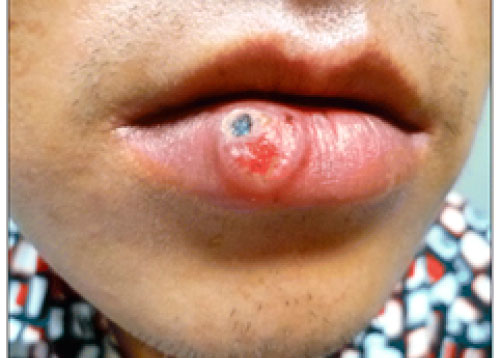
Image source: Qiao J, Fang H. Syphilitic chancre of the mouth. CMAJ. 2011;183(17):2015. doi:10.1503/cmaj.110664. Retrieved from https://www.cmaj.ca/content/183/17/2015.
Rectal syphilis sore
Here are rectal syphilis sores; 60% of people who contract syphilis don’t notice the primary syphilis lesion because of its location and the fact that it’s not painful.
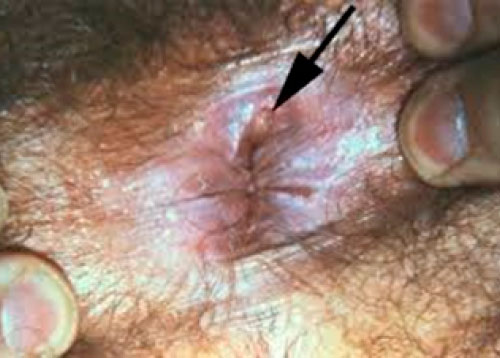
Image source: Syphilis—Primary (Anal Chancre) - MSD Manual Professional Edition. https://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/multimedia/image/v1023437. Accessed January 22, 2021.
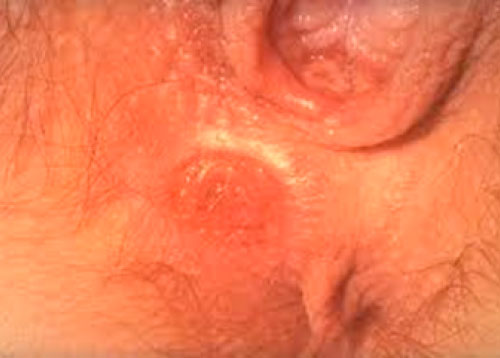
Image source: Chancre syphilitique= القرح الافرنجي الاولي. https://dermaamin.com/site/atlas-of-dermatology/3-c/248-chancre-syphilitique-.html. Accessed January 22, 2021.
Syphilis sore of the tongue
This image is of a syphilis sore on the tongue with well-defined borders and a clean base (there’s no pus).
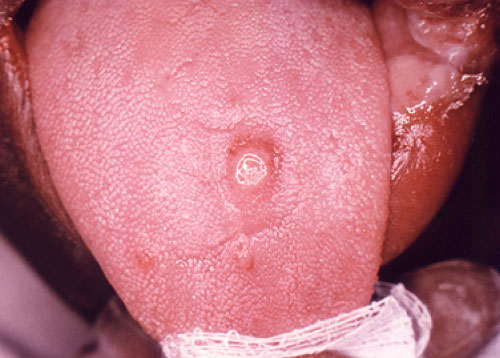
Image source: Division of STD Prevention, National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/images.htm
Syphilis sore of the tongue
Within a few weeks to a few months, 25% of people who contract syphilis will develop systemic symptoms that represent secondary syphilis. It is possible to have multiple episodes that resolve without treatment. Secondary syphilis can produce a wide variety of signs and symptoms:

Generalized symptoms
Patients with secondary syphilis can have systemic symptoms of fatigue, fever, body aches, and weight loss. These symptoms might be due to their body’s immune response to a widespread virus.
Lymph node enlargement
Half of people with secondary syphilis will have enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin area that are usually not tender (or only very mildly tender).
Skin rash
Rash is the most common sign of secondary syphilis—75% to 90% of people who have syphilis get it.
Of those, 20% don’t notice the rash because it can be very subtle and get better on its own.
A syphilis rash can take any form or shape. Any rash can be a syphilis rash.
The classic presentation of the syphilis rash is a rash that affects the entire torso and extremities, including the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. Rash on the palms and soles is a very important sign.
Usually, the rash is reddish-brown and 0.5 to 2 cm in diameter. Although it is usually scaly, it may be smooth.
Secondary syphilis rash
Widespread, brown reddish raised spots
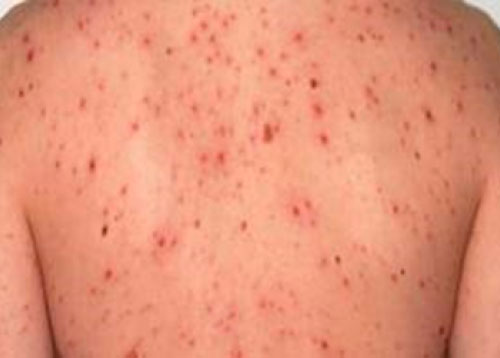
Image source: Syphilis: Signs, Symptoms, How To Test, Stages, Picture, Treatment, Curable? https://www.gentside.co.uk/health/syphilis-definition-symptoms-treatment-what-is-it_art154.html. Accessed January 22, 2021.
Secondary syphilis rash affecting the palms and soles
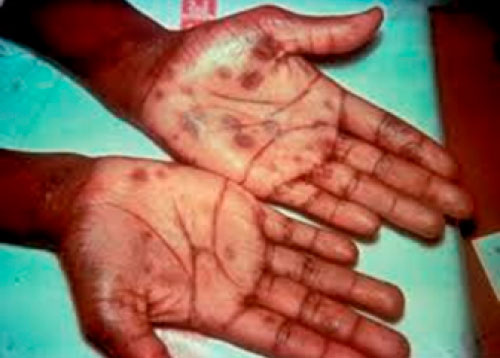
Image source: CDC/ NCHSTP/ Division of STD Prevention, STD Clinical Slides- Syphilis. https://www.cdc.gov/ std/training/clinicalslides/slides-dl.htm
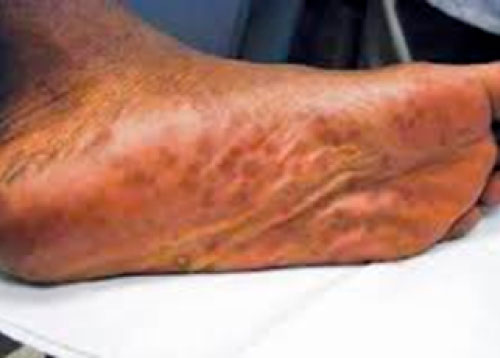
Image source: Division of STD Prevention, National Center for HIV/AIDS, Viral Hepatitis, STD, and TB Prevention, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/images.htm
Hair loss
Secondary syphilis presents in 10%–15% of people with so called “moth eaten” alopecia (hair loss).
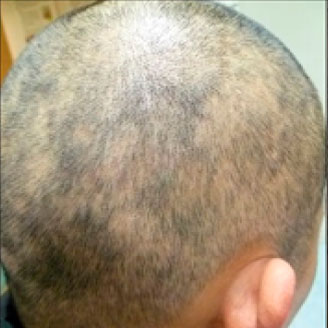
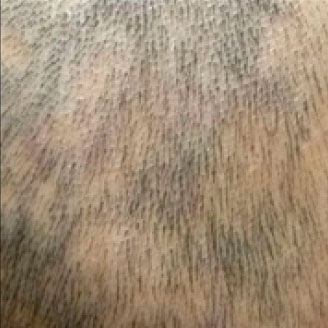
Image source: Qiao J, Fang H. Moth-eaten alopecia: A sign of secondary syphilis. CMAJ. 2013;185(1):61. doi:10.1503/cmaj.120229
Mucosal surfaces
Secondary syphilis can affect the oral mucosal surfaces—5% to 30% of patients may develop mucous patches, which are whitish erosions on the oral mucosa or tongue.
Photos of secondary syphilis white oral patches
They are very contagious.
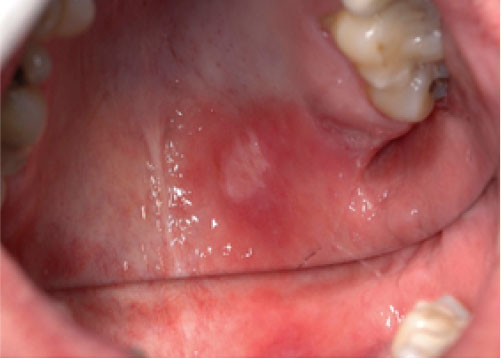
Image source: Hertel et al. Oral Syphilis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2013.
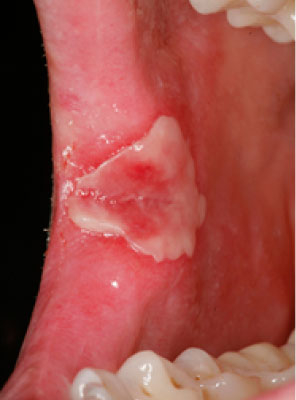
Image source: Hertel et al. Oral Syphilis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2013.
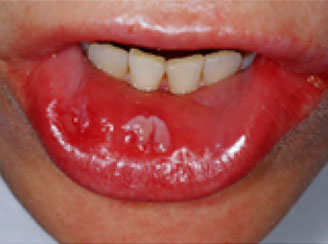
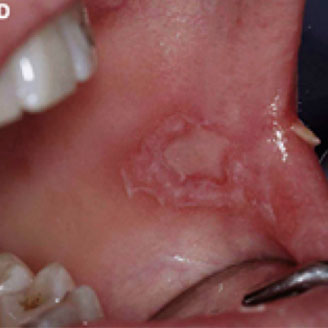
Image source: Hertel et al. Oral Syphilis. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2013.
Condylomata lata
Condylomata lata are large, raised, gray to white lesions that may develop in warm, moist areas such as the mouth and perineum. Five percent to 25% of patients with secondary syphilis get them.
They occur in areas containing a high concentration of syphilis infection and are highly contagious. Where they develop is believes to be close to the place where syphilis initially entered the patient’s body.
Photos of condylomata lata in the anal area
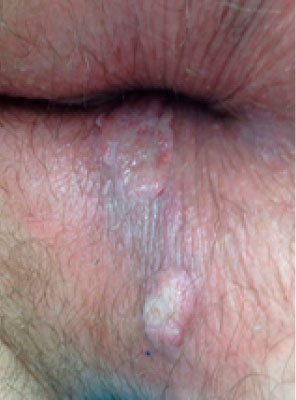
Image source: Bruins, F. G., Van Deudekom, F. J. A., & De Vries, H. J. C. (2015). Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ (Online), 350. https://www.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmj.h1259
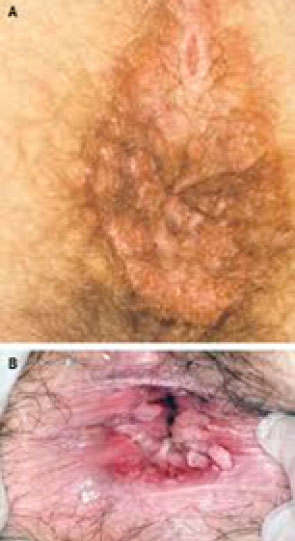
Image source: Bruins, F. G., Van Deudekom, F. J. A., & De Vries, H. J. C. (2015). Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ (Online), 350. https://www.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/bmj.h1259
Latent syphilis occurs when the patient has syphilis but no sign or symptoms of the disease. Syphilis in the latent stage can be diagnosed only through a blood test.
Latent syphilis can be early-stage or late-stage. This division is, of course, based on how long the patient has had syphilis.
Doctors assume the duration of syphilis based on the last negative syphilis test.
The division is important to the chance of syphilis transmission and the treatment.
Around 15% to 30 % of untreated syphilis patient will go into late-stage syphilis. In this stage, syphilis can damage the eyes, brain, nerve tissue, heart, blood vessels, bones, and joints.
Late-stage syphilis usually happens many years after the original untreated infection.

Get treated and/or tested for syphilis
Same day treatment and testing