Visual Comparison
(What Are the Differences and Similarities?)
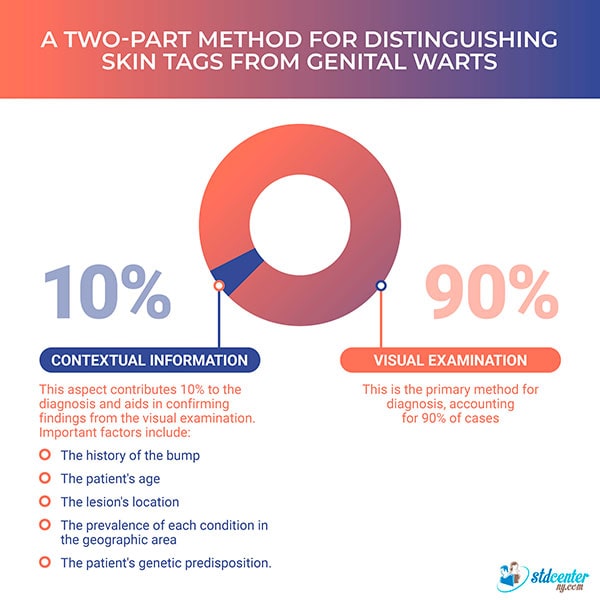
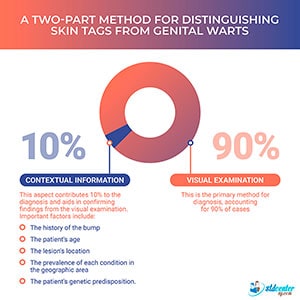
A visual skin inspection is crucial for accurate diagnosis and accounts for 90% of the differentiation between genital warts and skin tags.
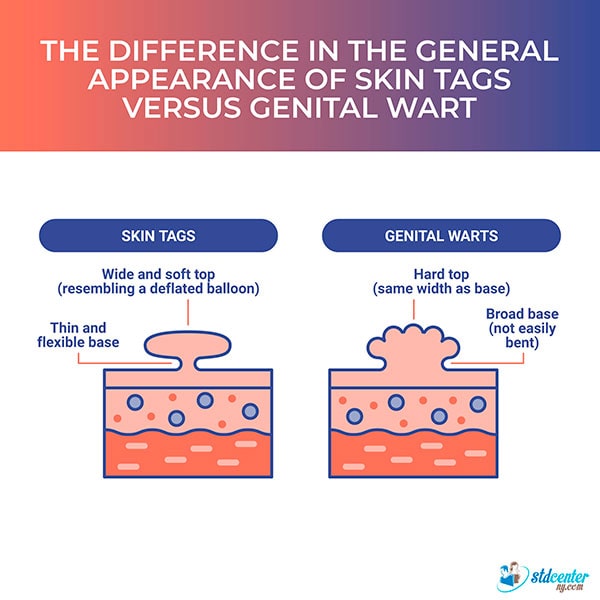
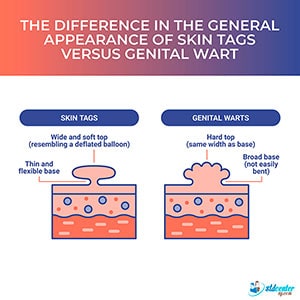
1. General Appearance
Skin Tags
Skin tags look like deflated balloons on thin stalks; their bases are slenderenoughtobend easily. [2] Skin Tags (Acrochordons) https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21528-skin-tags-acrochordons
Genital Warts
Unlike skin tags, genital warts are flat and have a wider base. They are usually anchored firmly to the skin. If the growth is pedunculated, featuring finger-like projections, the width of the skin lesion remains consistent at both the base and the top. This isdifferent from skin tags, which are wider at the top and have a significantly thinner base.
2. What is the Difference in Color?
Skin Tags
Skin tags come in various colors. They may match the patient's skin tone, which is rare, appear lighter, or be darker, which is the most common. The color of skin tags can change over time, but these alterations are generally not a cause for concern.
Genital Warts
Genital warts typically match the color of the patient's skin, although they can occasionally appear darker.
Color variation between genital warts and skin tags.
3. How Do They Feel When Touched?
Skin Tags
Skin tags have a very soft texture. They bend easily because they typically feature a thinner base and a larger top. [2] Skin Tags (Acrochordons) https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21528-skin-tags-acrochordons
Genital Warts
In contrast, genital warts possess a rough, bumpy surface that resembles cauliflower and are hard to the touch. They are generally flat, except when pedunculated, and due to their broader base, they do not move freely. [5] Genital Warts: Causes, Symptoms, preventions https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4209-genital-warts
Genital warts vs skin tag
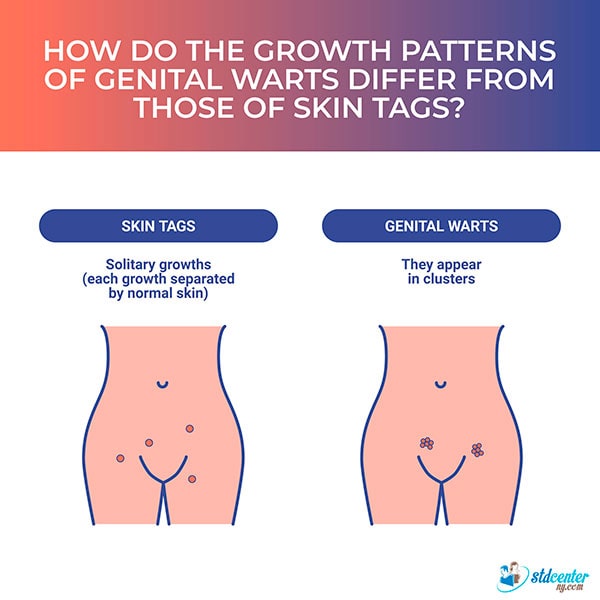
4. Growth pattern differences?
Skin Tags
Skin tags usually appear as isolated growths. When multiple skin tags are present, they are typically spaced apart by normal skin, leading to a widespread presence across various body parts simultaneously.
Genital Warts
In contrast, genital warts tend to group together. Unlike skin tags, genital warts can easily spread to nearby skin, especially through contact from scratching or shaving. However, they do not spread as easily to more distant areas of the body.
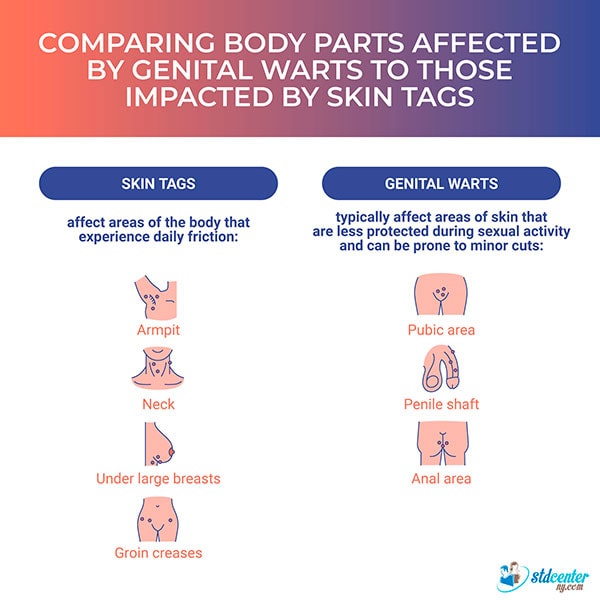
5. Which body parts are affected?
Skin Tags
Skin tags are often found in areas of the body that experience frequent friction, including the armpits, neck, beneath large breasts, and the groin creases.
Genital Warts
Genital warts are contagious and can spread through direct skin-to-skin contact. They usually affect areasof skin that are less protected during sexual activity and may be susceptible to minor cuts, including the pubic region, the shaft of the penis, and the surrounding anal area.
Contextual information or the "history of the bump” that distinguishes genital warts from skin tags.
Several important factors provide context for diagnosis: the history of the bump, including any changes in color and growth rate; the patient's age; the location of the skin lesion; the prevalence of certain conditions in the geographic area; and the patient's genetic predisposition.
This contextual information contributes 10% to the diagnosis, primarily helping to confirm the initial visual assessment.
Now, let's delve into each of these factors in more detail!


6. History of the Bumps
The history of this growth includes the following:
- Why was the growth noticed? (Are there any symptoms, or was it discovered accidentally?)
- How is it changing over time? (Is its appearance evolving? Is it getting bigger?)
Let's examine both questions regarding skin tags and genital warts.
Reasons for Noticing Bumps
Skin Tags
Skin tags are typically noticed when they are tugged. They often appear red, painful, and irritated.
Genital Warts
A sexually active person usually notices genital warts after a sexual encounter with someone they do not trust. However, these warts are typically not directly linked to a recent sexual encounter.
How Bumps Change Over Time
Skin Tags
Skin tags grow rapidly but eventually stop increasing in size. They may also change color over time. The growth of skin tags can continue until they are torn off or removed.
Genital Warts
Genital warts are slow-growing lesions that often appear weeks to months after infection. They can increase in size and spread to nearby skin through scratching or shaving. In some instances, they may start to shrink and disappear completely. As an infectious condition, genital warts can take the immune system up to two years to clear. However, the virus can remain dormant, with no visible skin growths, for a person's lifetime.
7. Is There an Age Difference Between Acquiring HPV and Developing Skin Tags?
Skin Tags
Skin tags generally occur in individuals over the age of 30 and are uncommon in younger people. As a person ages, their likelihood of developing skin tags increases. [1] Skin tags: why they develop and how to remove them. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/skin-tags
Genital Warts
Genital warts primarily affect sexually active individuals. Younger people, who tend to have multiple sexual partners, are at a higher risk of acquiring genital warts due to increased sexual activity at a younger age.
8. Prevalence of each condition?
Both skin tags and genital warts are quite common, with genital warts affecting a significantly larger proportion of the population:
Skin Tags:
Approximately 5% of individuals will eventually develop skin tags. [3] Skin tag: stat pearls https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547724/
Genital Warts (HPV):
An estimated 85% of individuals will contract genital warts during their lifetime.
9. Genetic predisposition
Skin Tags
Some individuals have a genetic predisposition to developing skin tags, indicating that those with a family history of these skin outgrowths are at a higher risk of experiencing them. [1] Skin tags: why they develop and how to remove them. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/skin-tags
Genital Warts
On the other hand, genital warts result from an infection. Anyone can contract them through contact with infected skin, and there is no genetic predisposition associated with theirdevelopment.
10. What are the causes of both conditions?
Skin Tags
The exact cause of skin tags remains unclear [1] Skin tags: why they develop and how to remove them. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/skin-tags , but several risk factors may contribute to their development:
- Friction from contact with fabric
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Advanced age
Genital Warts
Genital warts are primarily caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). While there are over 100 strains of HPV, two specific strains—type 6 and type 11—are predominantly responsible for genital warts. Fortunately, these strains are not associated with more severe health issues. [5] Genital Warts: Causes, Symptoms, preventions https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4209-genital-warts
Establishing Diagnosis
Most genital warts are diagnosed through a doctor'svisualexamination. If the diagnosisisuncertain, a skin biopsy may be performed. This minor procedure involves sending either the entire bump or part of it to a laboratory for microscopic analysis. It is typically performed in the doctor's office under local anesthesia.
Should You Get Treated?
Skin tags and most visible genital warts are generally benign, so treatment is optional. Here’s a closer look at the treatment options for both conditions:
Skin Tags
People often seek treatment for skin tags for various reasons:
- Irritation: If skin tags frequently get caught on clothing or jewelry, they can become irritated.
- Aesthetic Concerns: Some individuals dislike the appearance of skin tags.
Genital Warts
Due to the infectious nature of genital warts, many seek treatment to prevent local spread and minimize the risk of transmission to partners.
[4, 5]
Genital warts
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/genital-warts/symptoms-causes/syc-2035523
Genital Warts: Causes, Symptoms, preventions
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4209-genital-warts
How are these bumps treated?
The treatment for genital warts and skin tags [1] Skin tags: why they develop and how to remove them. https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/skin-tags is the same and is very effective. The goal is to remove the skin tag or genital wart using one of the following methods:
1. Cryotherapy. Cold liquid nitrogen is applied to freeze and destroy the lesion.
2. Surgery. The lesion is removed by cutting it with a scalpel or scissors, a minor in-office procedure.
3. Laser Treatment. Direct rays of light are used to burn away the tag or wart.
4. Acid Treatment. An application of trichloroacetic acid (TCA) destroys the tag or wart.
Can HPV and Skin Tags Be Prevented?
Skin Tags
The exact causes of skin tags are not well understood. Various factors may contribute to their development, so they are generally not preventable.
Genital Warts
In contrast to skin tags, genital warts can be prevented [5] Genital Warts: Causes, Symptoms, preventions https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4209-genital-warts , or more accurately, the risk of contracting them can be reduced through the following measures:
1. Getting vaccinated
2. Using protection during sexual activity
Source
-
Skin tags: why they develop and how to remove them.
https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/skin-tags -
Skin Tags (Acrochordons)
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21528-skin-tags-acrochordons -
Skin tag: stat pearls
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547724/ -
Genital warts
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/genital-warts/symptoms-causes/syc-2035523 -
Genital Warts: Causes, Symptoms, preventions
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4209-genital-warts -
Genital warts: stats pearl
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441884/