> ARTICLES
STDs that cause sore throat
Chlamydia
According to recent statistics, chlamydia is the most commonly reported bacterial sexually transmitted infection in the United States, with over 1.6 million cases reported each year, and that number is growing every year. There are three types of chlamydia bacteria. The one that causes an STD is called Chlamydia Trachomatis.
[1, 2]
STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2021. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm#:~:text=The%20report%20indicates%20that%20in,return%20to%20pre%2Dpandemic%20levels.
Getting infected with oral chlamydia
According to the CDC, someone may get throat chlamydia when, during sex, oral mucosa comes into contact with: [1] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
✓ Penis
✓ Anus
✓ Vagina
Chance of contracting chlamydia orally
The exact likelihood of contracting oral chlamydia is unknown (though it is estimated to be low). However, oral chlamydia is much less common than genital and anal infections because the bacteria that causes the infection "prefers" the genital and anal areas. Additionally, oral chlamydia testing is not common; the disease is usually asymptomatic (in over 95% of cases) and goes away on its own within six weeks of infection. Thus, cases of oral chlamydia are underreported, making it challenging to study and estimate transmission rates. [3] Routine universal testing versus selective or incidental testing for oropharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis in women in the Netherlands: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet Infextious Diseases https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1473309921004655
Certain factors may increase the risk of getting oral chlamydia. Those are:
[1, 4]
STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
Pharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis in Men Who Have Sex With Men (MSM) in The Netherlands: A Large Retrospective Cohort Study. PubMed Central
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9049257/
✓ Exposure to ejaculate or vaginal fluids (infection can be present in genital fluids).
✓ Having multiple oral sex partners.
✓ The presence of other oral STDs, such as oral herpes or syphilis.
Frequency of oral chlamydia for different genders and sexual orientations
According to available data, the prevalence of oral chlamydia for different groups of people is as follows: [5] Extragenital Infections Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: A Review of the Literature. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4913006/
✓ 0.2-3.2% of women.
✓ 0–22.0% of men having sex with women (MSW).
✓ 0–3.6% of men having sex with men (MSM).
A study conducted in Sweden showed that among patients with genital chlamydia, throat chlamydia was diagnosed in 2.7% and 7% of men and women, respectively. [6] Pharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis is not uncommon anymore. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases https://sci-hub.se/https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2011.553243
It is also worth noting that around 32% of women with throat chlamydia do not have concurrent anal or genital chlamydia. This fact highlights the importance of testing for oral STDs, even if the tests for anogenital STDs are negative. [3] Routine universal testing versus selective or incidental testing for oropharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis in women in the Netherlands: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet Infextious Diseases https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1473309921004655
Incubation period
For symptomatic people, it usually takes around 1-3 weeks for symptoms of oral chlamydia to develop.
Symptoms
In the majority of cases, people with oral chlamydia have no symptoms. Research shows that only 2-5% of oral chlamydia cases cause symptoms of pharyngitis or lymphadenitis.
These symptoms may include:
[3, 6]
Routine universal testing versus selective or incidental testing for oropharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis in women in the Netherlands: a retrospective cohort study. The Lancet Infextious Diseases
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1473309921004655
Pharyngeal Chlamydia trachomatis is not uncommon anymore. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases
https://sci-hub.se/https://doi.org/10.3109/00365548.2011.553243
✓ Sore throat (which can be confused with flu or strep throat)
✓ Redness and inflammation of the back of the throat
✓ Swollen tonsils
✓ Difficulty swallowing
✓ Mild fever and fatigue
Complications
In about 36–57% of cases, infected people get rid of oral chlamydia without any treatment within 9–10 days (most cases resolve within six weeks of exposure). However, in some cases, this condition can cause complications such as gingivitis (gum infection) and periodontal disease (chronic inflammation of gums and other structures around the teeth), resulting in secondary mouth infections and tooth loss. [4] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
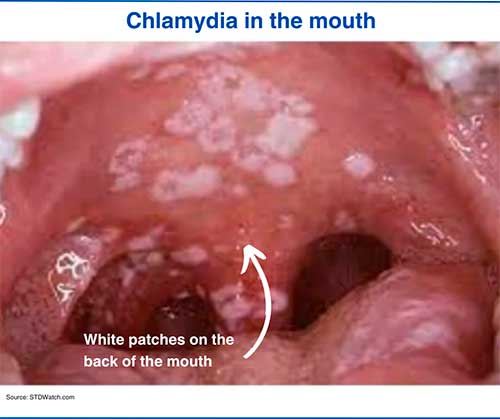
Oral Chlamydia pictures
1. Chlamydia sore throat
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is an STI caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae that affects genital, oral, and anal regions. Annually, around 710,000 gonorrhea cases are reported in the US, making it the second most common bacterial STD after chlamydia. [5] Sexually Transmitted Disease Surveillance 2021. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). https://www.cdc.gov/std/statistics/2021/default.htm#:~:text=The%20report%20indicates%20that%20in,return%20to%20pre%2Dpandemic%20levels.
Getting infected with oral gonorrhea
A person can contract oral gonorrhea when the oral mucosa comes into contact with gonorrhea-infected areas: [1] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
✓ Vagina
✓ Anus
✓ Penis
Chance of contracting gonorrhea orally
It is difficult to determine the exact chance of contracting throat gonorrhea from a single oral intercourse since oral gonorrhea testing is not routinely performed, and the infection often goes undetected. However, it is estimated that the overall chance of getting oral gonorrhea can be relatively high, especially among the MSM population. [7] Factors associated with pharyngeal gonorrhea in young people: Implications for prevention. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6086760/
Additional factors that can significantly increase the risk of gonorrhea contraction are: [7] Factors associated with pharyngeal gonorrhea in young people: Implications for prevention. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6086760/
✓ Having multiple oral sex partners. Research shows that people who have had 5 or more oral sex partners over three months are about 6 times more likely to contract oral gonorrhea than those who have only one oral sex partner.
✓ Being exposed to an ejaculate (or pre-ejaculate) or vaginal fluids. Those who are exposed to semen (cum) or vaginal secretions during oral sex are about 3 times more likely to contract oral gonorrhea than those who are not. What's more, the chances are even higher among those who report swallowing semen (cum) or vaginal fluids.
Frequency of oral gonorrhea for different genders and sexual orientations
The overall prevalence of oral gonorrhea among different population groups is as follows: [5] Extragenital Infections Caused by Chlamydia trachomatis and Neisseria gonorrhoeae: A Review of the Literature. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4913006/
✓ 2-10% of women.
✓ 3-7% of men who have sex with women (MSW).
✓ 2-11% of men who have sex with men (MSM).
Importantly, around 10- 20% of women diagnosed with cervical gonorrhea also suffer from gonorrhea of the throat. Therefore, women who test positive for genital gonorrhea and who also engage in oral sex should get tested for oral gonorrhea. [5] Diagnosis and Management of Gonococcal Infections. American Academy of Family Physicians https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2012/1115/p931.html
Incubation period
The incubation period for oral gonorrhea is around seven days.
Symptoms
Up to 90% of men and women with throat gonorrhea are asymptomatic. [5] Diagnosis and Management of Gonococcal Infections. American Academy of Family Physicians https://www.aafp.org/pubs/afp/issues/2012/1115/p931.html
In symptomatic patients, throat gonorrhea symptoms are nonspecific and include:
✓ Sore throat
✓ Redness in the throat
✓ Mild fever
✓ Swollen tonsils
✓ Difficulty swallowing
✓ Burning sensation in the throat
Complications
If left untreated, oral gonorrhea may persist for as long as 16 weeks, which may result in its further transmission to sexual partners as well as spread through the bloodstream, causing severe complications such as:
[1, 9]
STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
The Duration of Pharyngeal Gonorrhea: A Natural History Study. PubMed Central
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8366826/
✓ Skin rash
✓ Joint pain
✓ Heart infection (potentially life-threatening)
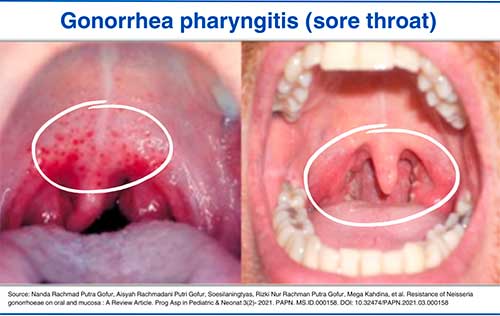
Oral Gonorrhea pictures
1. Gonorrhea sore throat
Syphilis
Syphilis is a common STD caused by the bacteria called Treponema pallidum. In 2021, 176,700 syphilis cases have been reported in the US. The disease develops in stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary, each with a different manifestation. [2] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
Getting infected with syphilis orally
Around 14% of syphilis cases are caused by oral sex. Oral transmission of syphilis occurs when, during oral sex, the syphilitic lesion (chancre) comes into direct contact with intact skin or mucous membrane. [10] Transmission of Primary and Secondary Syphilis by Oral Sex --- Chicago, Illinois, 1998—2002. CDC https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/mm5341a2.htm
There is also evidence that in very rare cases, syphilis can be transmitted through kissing if the infected person has a chance on the lips, throat, or mouth. [11] Oral manifestations of syphilis. Elsevier https://www.elsevier.es/en-revista-clinics-22-articulo-oral-manifestations-of-syphilis-S1807593222029878#:~:text=Oral%20lesions%20arise%20in%20at,nodular%20lesions%20may%20rarely%20arise
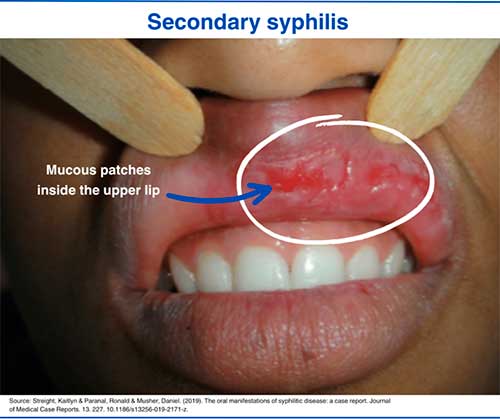
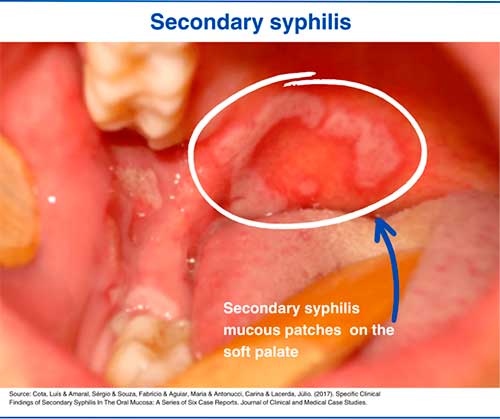
The incidence of oral syphilis has been increasing in recent years, and it has been established that oral infection most often affects the tongue (37.5% of cases), lips (29.5% of cases), palate (19.3% of cases), and the buccal mucosa (6.8% of cases). [12] Oral Manifestations of Early Syphilis in Adults: A Systematic Review of Case Reports and Series. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8594522/
Chance of contracting syphilis orally
The per-intercourse probability of transmission of oral syphilis during penile-oral sex in the primary and secondary stages is around 1%. [13] Resurgence of Syphilis in the United States: An Assessment of Contributing Factors. Sage Journals. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/1178633719883282#:~:text=Sexual%20networks,-The%20ability%20of&text=In%20a%20study%20by%20Gray,per%20penile%2Doral%20sexual%20act
The likelihood of transmission of oral syphilis through oral-vaginal or oral-anal intercourses has not yet been established.
However, the risk of contracting oral syphilis may be increased in case of:
✓ Presence of cuts or sores in the mouth
✓ Having oral sex with a partner who has primary or secondary stages of syphilis (especially if there is a syphilitic chancre on the genitals).
Incubation period
The incubation period of syphilis (the period between exposure and the development of syphilitic chancre) is about 1–3 weeks. [11] Oral manifestations of syphilis. Elsevier https://www.elsevier.es/en-revista-clinics-22-articulo-oral-manifestations-of-syphilis-S1807593222029878#:~:text=Oral%20lesions%20arise%20in%20at,nodular%20lesions%20may%20rarely%20arise
Symptoms
There are 4 stages of syphilis, which have different signs and symptoms. The initial stage of the disease is called primary syphilis, which is characterized by the appearance of a single (in most cases) painless ulcer (chancre) on the site of exposure. In the case of oral syphilis, this syphilitic chancre typically appears on the lip, rarely on the tongue or throat. The chancre is round and deep with irregularly raised borders and a red or purple base. In men, it is most commonly located on the upper lip, and in women, it is on the lower lip. This fact can be explained by the different techniques of performing fellatio and cunnilingus. [11] Oral manifestations of syphilis. Elsevier https://www.elsevier.es/en-revista-clinics-22-articulo-oral-manifestations-of-syphilis-S1807593222029878#:~:text=Oral%20lesions%20arise%20in%20at,nodular%20lesions%20may%20rarely%20arise
The chancre will go away with or without treatment within 3-6 weeks. [14] Syphilis – CDC Basic Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm However, if left untreated within 8 weeks of primary syphilis, the infection will enter the bloodstream and develop into a systematic infection with generalized symptoms. These symptoms include:
✓ Sore throat
✓ Fever
✓ Fatigue
✓ Weight loss
✓ Muscle and joint pain
✓ Patchy hair loss
✓ Brownish spots on the palms and soles
As with the primary stage, these symptoms will also resolve on their own but will eventually develop into further stages, causing life-threatening complications. [14] Syphilis – CDC Basic Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm
Complications
Syphilis is a serious infection. If left untreated, it can lead to death or fatal complications such as: [1] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
✓ Damage to internal organs
✓ Dementia
✓ Blindness
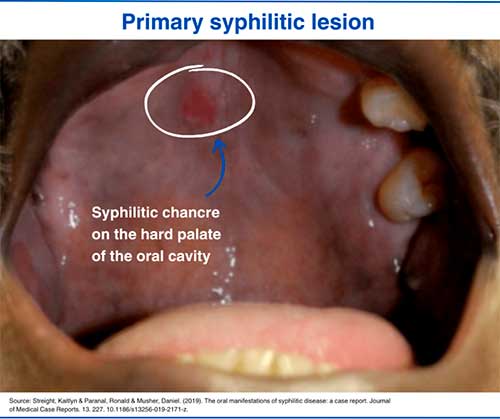
Oral Syphilis pictures
1. Primary syphilis lesion
2. Secondary syphilis mucosal patches
Herpes
Herpes is a highly contagious viral infection that causes cold sores (fever blisters). Herpes is caused by two types of herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection, namely HSV-1 and HSV-2. Both types can affect both oral and genital regions. However, HSV-1 most often affects the oral region, while HSV-2 affects the genitals. Herpes is incurable; once infected, it will remain in the body for the rest of your life. [15] Herpes Simplex Virus. WHO https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/herpes-simplex-virus
Getting infected with oral herpes
Oral herpes is spread through skin-to-skin contact.
More specifically, the infection can be transmitted via:
[16, 17]
Oral Herpes. Johns Hopkins Medicine
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/herpes-hsv1-and-hsv2/oral-herpes
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) Mouth Infection. University of Rochester Medical Center
https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/encyclopedia/content.aspx?ContentTypeID=85&ContentID=P00888
✓ Kissing someone infected with oral herpes (especially when they have cold sores).
✓ Giving oral sex to somebody with genital herpes.
✓ Non-sexual contact, for example, touching infected skin, sharing infected objects (such as razors or lip balms) with someone who has herpes, and non-sexual kissing (such as kissing on the cheek).
Chance of contracting herpes orally
Data on the per-exposure likelihood of herpes transmission through oral sex is not well defined since it is difficult to determine how exactly someone got the infection (herpes infection is widespread and can be transmitted even through non-sexual contact (e.g., kissing, sharing a lip balm or utensils)). Either way, the likelihood of contracting herpes through oral intercourse is likely high, as the infection is highly contagious. [18] Cold sore. Mayo Clinic https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/cold-sore/symptoms-causes/syc-20371017
Different factors can increase the chance of herpes transmission. For example:
✓ Presence of herpes sores in herpes-positive individual
✓ Presence of sores or cuts on the lips and in the mouth of a healthy individual
✓ Direct contact with fluids coming out from the sores
Frequency of oral herpes
Oral herpes is known to be highly contagious, with the HSV-1 virus alone affecting more than 67% of the world's population aged 50 years or younger. [15] Herpes Simplex Virus. WHO https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/herpes-simplex-virus In the US, the estimated percentage of the population with oral herpes ranges from 50-80%.
Incubation period
The incubation period (the period between exposure and the appearance of cold sores) of oral herpes ranges from 2 to 12 days (4 days on average).
Symptoms
Most herpes-positive people are unaware of their infection, as about 90% of all herpes cases do not cause noticeable symptoms. [19] Herpes: The Blistering Facts. University of Utah ttps://healthcare.utah.edu/healthfeed/2015/11/herpes-blistering-facts
For the rest, symptoms of the initial infection (first outbreak) include: [16] Oral Herpes. Johns Hopkins Medicine https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/herpes-hsv1-and-hsv2/oral-herpes
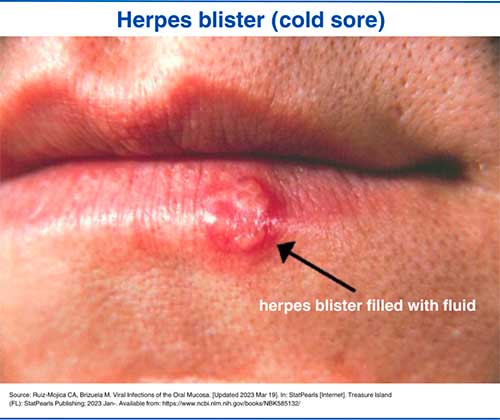
✓ Cold sores (painful blisters filled with fluid) on the lips, tongue, gums, and throat. These sores break within two days, then form a crust and heal on their own within two weeks.
✓ Flu-like symptoms
✓ Swollen lymph nodes
✓ Headache
✓ Fever
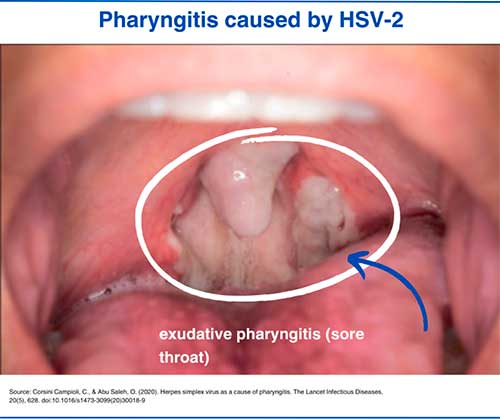
✓ Sore throat
Complications
In rare occasions, the herpes virus affects the eyes of the infected person, leading to eye infection, which may result in scaring of the surface of the eye, vision problems, and blindness. [1] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
Oral herpes pictures
1. Herpes blister (cold sore)
2. Herpetic pharyngitis (sore throat)
HPV
HPV (Human Papillomavirus) is the most commonly occurring STI globally. Around 90% of males and 80% of females acquire this infection at least once. 20 Of the 200 known types of HPV, four affect the mucous membranes of the mouth and genitals, nine of which can cause cancer. [21] Oropharyngeal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection. Cleveland Clinic https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15010-oropharyngeal-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-infection#:~:text=What%27s%20the%20oral%20HPV%20incubation,t%20develop%20symptoms%20at%20all
Getting infected with oral HPV
Oral HPV is transmitted via skin-to-skin (mucosa-to-mucosa) contact. Therefore, someone may contract the oral infection through: [22] Oral Human Papillomavirus Infection University of California San Francisco https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/oral-human-papillomavirus-infection
✓ Oral sex (oral-genital, oral-anal contact)
✓ Deep kissing (especially prolonged tongue-to-tongue contact)
Certain factors increase the risk of getting oral HPV. Those are: [22] Oral Human Papillomavirus Infection University of California San Francisco https://www.ucsfhealth.org/medical-tests/oral-human-papillomavirus-infection
✓ Having multiple sexual partners
✓ Smoking and alcohol consumption
✓ Having weak immunity
In addition, males are more susceptible to oral HPV infection than females.
Chance of contracting HPV orally
The exact likelihood of HPV transmission through oral sexual intercourse has not yet been established. The thing is that oral HPV testing is not part of routine STD screening. Also, in 90% of cases (9 out of 10), HPV resolves on its own without causing any symptoms or complications and therefore goes unnoticed. [23] Genital HPV Infection – Basic Fact Sheet.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). https://www.cdc.gov/std/hpv/stdfact-hpv.htm
Anyways, the transmission rate is estimated to be high since the infection is highly contagious, and almost every sexually active person contracts the disease at least once in a lifetime.
Frequency of oral HPV for different genders
The prevalence of oral HPV is 11.5% and 3.2 % among men and women, respectively. [24] Prevalence of Oral HPV Infection in Men & Women. MDedge. https://www.mdedge.com/internalmedicine/clinical-edge/summary/infectious-diseases/prevalence-oral-hpv-infection-men-women
Research shows that about 19.3% of men and 5.1% of women with genital HPV have oral HPV. [25] Transmission and clearance of human papillomavirus infection in the oral cavity and its role in oropharyngeal carcinoma – A review. PubMed Central https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10078185/ At the same time, the prevalence of oral HPV without concurrent genital infection was only 4.4% and 2.1% among men and women, respectively. [26] Differences in Prevalence Between Sexes and Concordance With Genital Human Papillomavirus Infection, NHANES 2011 to 2014. PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6203692/
Incubation period
Symptomatic patients typically develop oral HPV symptoms within 3 to 6 months of infection. [21] Oropharyngeal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection. Cleveland Clinic https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15010-oropharyngeal-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-infection#:~:text=What%27s%20the%20oral%20HPV%20incubation,t%20develop%20symptoms%20at%20all
Please note that most of the oral HPV cases are asymptomatic, and the virus can remain in the tissues of the oral cavity without causing any noticeable signs or symptoms.
Symptoms
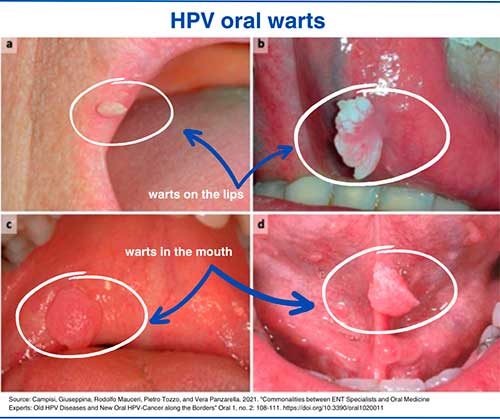
In most cases, the immunity fights HPV infection before the virus causes signs or symptoms. However, some people develop oral warts caused by the virus, which are characterized as tiny, flesh-colored bumps appearing anywhere in the oral cavity. [21] Oropharyngeal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection. Cleveland Clinic https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15010-oropharyngeal-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-infection#:~:text=What%27s%20the%20oral%20HPV%20incubation,t%20develop%20symptoms%20at%20all
Complications
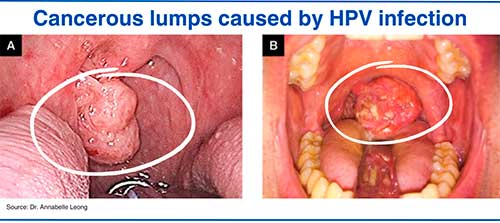
Rarely (in about 1% of cases) oral HPV infection can lead to oropharyngeal cancer, the symptoms of which include: [21] Oropharyngeal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection. Cleveland Clinic https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15010-oropharyngeal-human-papilloma-virus-hpv-infection#:~:text=What%27s%20the%20oral%20HPV%20incubation,t%20develop%20symptoms%20at%20all
✓ Cough
✓ Weight loss
✓ Persistent sore throat
✓ Hoarseness
✓ Coughing up blood
✓ Pain or discomfort while swallowing
✓ Swollen lymph nodes
The majority of oropharyngeal cancers are caused by HPV-16 infection.
Oral HPV pictures
1. HPV oral warts
2. HPV oral cancer
HIV
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) is a potentially deadly infection that affects more than 39 million people worldwide. This infection attacks white blood cells responsible for regulating immune responses, weakening the immune system and making a person more susceptible to various infectious (viruses, fungi, and bacteria) and non-infectious (for example, cancer) diseases. [27] HIV and AIDS. WHO. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids
HIV can be transmitted through body fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal secretions, and breast milk, as well as through mother-to-child transmission.
Oral Transmission of HIV
Theoretically, oral transmission of HIV is possible through: [1] STD Risk and Oral Sex – CDC Fact Sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) https://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/stdfact-stdriskandoralsex.htm
✓ Mouth-to-vagina contact (risk very low, especially with oral sex)
✓ Mouth-to-penis contact
✓ Mouth-to-anus contact
Certain factors increase the risk of oral transmission of HIV, such as:
✓ Presence of mouth ulcers or bleeding gums.
✓ Infection with other STDs.
✓ Presence of ulcers on the genitals.
Chance of contracting HIV orally
The risk of acquiring HIV through oral intercourse is considered very low and virtually impossible if the infected partner's viral load is so low that it is undetectable. Oral intercourse carries a much lower risk of transmitting HIV than anal or vaginal intercourse. According to the literature, the estimated probability of contracting HIV per unprotected oral sex is 0.04%. [28] Oral sex and the risk of HIV transmission. Aidsmap. https://www.aidsmap.com/about-hiv/oral-sex-and-risk-hiv-transmission
Incubation period
The incubation period of HIV ranges between 1-6 weeks. However, having detectable antibodies in the blood will take 1-3 months. [29] HIV/AIDS. National Centre for Infectious Diseases https://www.ncid.sg/Health-Professionals/Diseases-and-Conditions/Pages/HIV-AIDS.aspx#:~:text=Incubation%20Period&text=Between%201%20and%206%20weeks,within%2010%20years%20after%20infection
Symptoms
HIV symptoms vary from person to person and from stage to stage. Symptoms of HIV affecting the oral cavity appear early in the infection, also known as acute HIV infection (within four weeks of infection).
Acute HIV
Up to 90% of people with acute HIV infection develop flu-like symptoms. These symptoms last for a few days (sometimes for a few months) and include: [30] Symptoms of HIV. HIV.gov https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/symptoms-of-hiv
✓ Sore throat
✓ Muscle and joint pain
✓ Headache
✓ Skin rash
✓ Swollen lymph nodes
✓ Night sweats
✓ Mouth ulcers
✓ Extreme tiredness and fatigue
Complications
The most common complications of AIDS are opportunistic infections (infections that typically do not cause disease in healthy people but may result in severe complications in people with weakened immunity). People with AIDS may also develop various types of cancer.
[27, 30]
HIV and AIDS. WHO.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hiv-aids
Symptoms of HIV. HIV.gov
https://www.hiv.gov/hiv-basics/overview/about-hiv-and-aids/symptoms-of-hiv
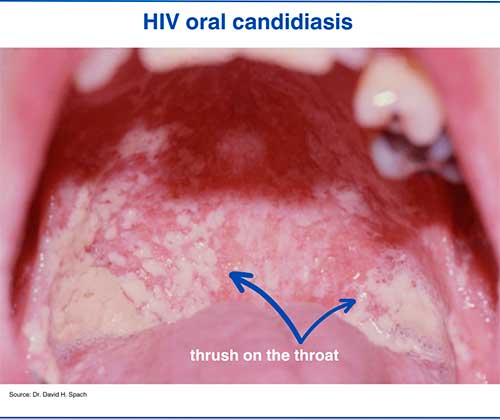
Oral HIV pictures
1. HIV oral thrush